Indian GPS NavIC to be linked to Aadhaar enrolment devices
Context
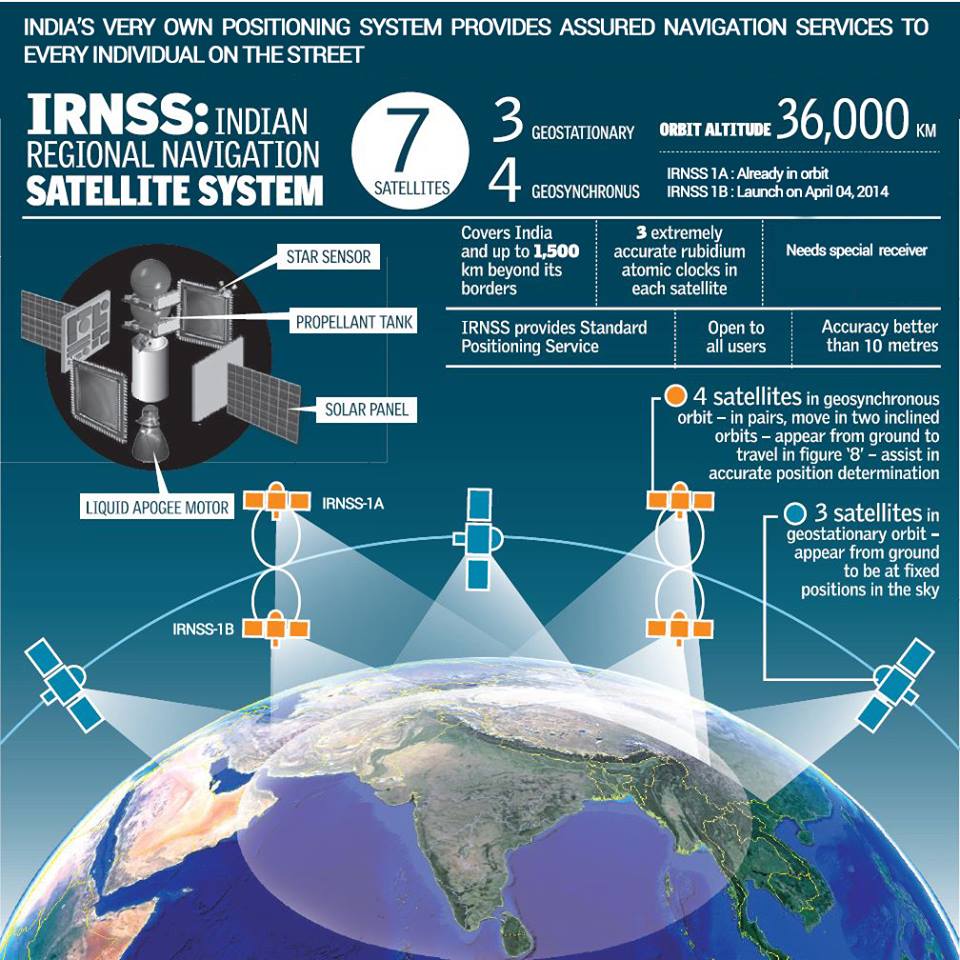
The Department of Space (DoS) informed the Parliamentary Committee of Science and Technology that the seven-satellite Navigation with Indian Constellation (NavIC), India’s equivalent of the American GPS (global positioning system), will soon be integrated into Aadhaar enrollment devices throughout the nation.
What is NavIC?
The Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO) created the autonomous regional satellite navigation system known as NavIC, or Navigation with Indian Constellation. Over the Indian subcontinent and an area that reaches about 1,500 kilometers (930 miles) beyond its borders, it offers precise real-time positioning and timing services. The system is made to provide navigation services to authorized users, including the military and civilians.
What is the key uses of NavIC?
- Maps and Navigation: The main objective of NavIC is navigation. It facilitates safe and effective transportation by assisting people, things, ships, and aircraft in determining their precise location, speed, and direction. It also helps in the production of precise geographical data and maps.
- Transportation: By directing vehicles, such as cars, buses, trucks, and trains, to take the best routes, the system improves transportation networks. As a result, fuel is saved, travel times are shortened, and productivity is increased.
- Agriculture: Based on precise positioning and timing data, NavIC can be utilized in precision agriculture to help farmers optimize crop planting, watering, and harvesting.
- Disaster Management: NavIC enables emergency response teams to more efficiently discover affected areas, analyze the situation, and coordinate relief activities during catastrophes or natural disasters.
- time and Synchronization: For telecommunications networks, financial transactions, power grid synchronization, and scientific operations that call for exact time, accurate timing from NavIC is essential.
- Geodesy and surveying: The system helps geodesists, builders, and land surveyors measure angles and distances correctly for mapping, construction, and geodetic surveys.
- Marine Navigation: NavIC aids in maritime navigation by directing boats and ships, improving safety, and lowering the possibility of collisions.
- Aviation: NavIC helps the aviation industry by giving pilots, air traffic controllers, and aviation systems precise navigational information for safe and effective flight operations.
- Fleet management :Fleet management firms, such logistics and transportation firms, can utilize NavIC to plan routes, track the whereabouts of their vehicles, and boost the efficiency of their fleets as a whole.
- Scientific research :Geophysical and environmental research are just two examples of the many scientific investigations that may be conducted using NavIC’s accurate positioning data.
- Military and Security: The military and authorized security professionals may use the limited service of NavIC for strategic and defense-related purposes.
What is the significance of having NavIC?
- Strategic Independence: In terms of satellite navigation technology, NavIC gives India strategic independence. It lessens reliance on external navigation systems and guarantees that the nation has access to accurate positioning and timing data for a variety of purposes, including defense.
- Sovereignity and security:India’s sovereignty and security are improved by having its own navigation system. Even in times of conflict or catastrophe, it makes sure that vital industries like communication, transportation, and defense have access to precise and secure positional data.
- National Development: NavIC promotes national development by enhancing agriculture practices, assisting in disaster management, and supporting infrastructure projects. It improves both the economy and everyone’s quality of life.
- Disaster Response: NavIC’s precise positioning data is essential for disaster response and relief operations. During natural catastrophes, it facilitates effective coordination of rescue operations, planning of response plans, and localization of impacted areas by emergency services.
- Agricultural Productivity: NavIC supports precision farming in a nation like India that is predominately agrarian. Based on precise geolocation data, farmers may optimize their irrigation, fertilizing, and planting schedules, increasing crop yields.
Other Examples of navigational systems:
- GPS:The most well-known and commonly used worldwide satellite navigation system is the worldwide Positioning System (GPS), which was created and is maintained by the United States. It is made up of a constellation of satellites that offer precise timing, positioning, and navigational services all over the world.
- GLONASS: Another worldwide satellite navigation system created by Russia is GLONASS. It gives coverage of Russia and the areas around it and offers precise positioning and timing services.
- Galilio:Galileo is a global navigation system created by the European Union that aims to offer accurate location and timing data. It provides services to civilians and authorized users and seeks to outperform current systems in terms of accuracy and coverage.
- BeiDou Navigation Satellite System (BDS): China developed the global satellite navigation system known as the BeiDou Navigation Satellite System (BDS), which provides positioning, navigation, and timing services. In order to cover China and the entire world, it comprises of both regional and global constellations.
- Quasi-zenith satellite system: Regional satellite navigation system QZSS, run by Japan, is created to offer improved coverage across Japan and nearby areas. It collaborates with other worldwide navigation systems to increase availability and accuracy.