India, Japan will work to strengthen ‘peacetime cooperation’: Jaishankar
Context:
Jaishankar, India’s minister of external affairs, avoided a question about how the two nations would cooperate in the event of a conflict in the Taiwan Strait or between India and China at the Line of Actual Control (LAC) on Friday by saying that India and Japan would prefer to work to strengthen their “peacetime cooperation”.
Indo-Japan Relationship
- Historical Relationships: Buddhism has played a significant role in centuries of cultural and religious exchanges between India and Japan. The basis for cross-cultural collaboration and understanding is this common heritage.
- Strategic Convergence: India and Japan share a common strategic interest in seeing the Indo-Pacific region remain peaceful and stable. They are both concerned about the region’s need for a rules-based system as well as maritime security, freedom of navigation, and other related issues.
- Economic Collaboration:
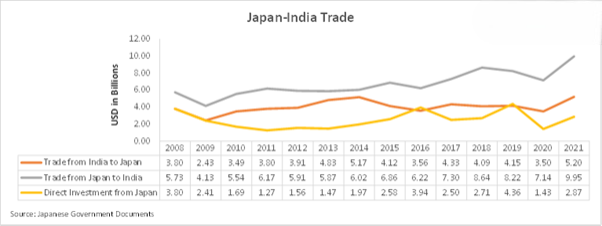
- Japan is a big investor in India and has been instrumental in advancing India’s infrastructure. Japanese businesses have made investments in a variety of industries, including manufacturing, transportation, and technology.
- To increase their bilateral commerce and investment, the two nations have signed several economic accords.
- Special Strategic and Global Partnership: 2014 saw the reclassification of India and Japan’s partnership to a “Special Strategic and Global Partnership.” This represents a strengthening of ties and a commitment to increase cooperation in several areas.
- Defense Relations:
- To improve maritime security and interoperability between their armed forces, both nations regularly engage in joint military exercises and naval drills.
- India’s request for a permanent seat on the UN Security Council has received backing from Japan.
- Quad Partnership:
- The Quadrilateral Security Dialogue, sometimes known as the Quad, consists of Japan, India, the United States, and Australia. The Indo-Pacific area should be free, open, and inclusive to ensure peace and development.
- The Quad has also taken part in projects aimed at improving infrastructure and providing aid in case of emergencies.
- Nuclear Cooperation: In 2016, India and Japan inked a civil nuclear cooperation deal that allows Japan to provide nuclear technology and fuel to India, improving the energy security of that country.
- Cultural Exchanges:
- Both nations actively support cultural exchanges, which can take the form of academic partnerships, film festivals, and art exhibitions. These interactions strengthen interpersonal relationships and increase knowledge.
- To provide technical training for Indian youth, the Japanese government established the Japan-India Institutes for Manufacturing (JIM) and Japan-India Institutes of Information and Communication Technology (JIT) in India.
- Regional Connectivity and Infrastructure Projects: Japan has contributed to several infrastructure projects in India, notably the Delhi-Mumbai Industrial Corridor (DMIC) and the Mumbai-Ahmedabad High-Speed Rail Project (Bullet Train). These initiatives seek to increase regional connectivity and economic growth.