Controlling Inflation
Context:
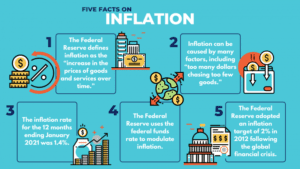
- The recent action of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) to raise the repo rate by 40 basis points and cash reserve ratio (CRR) by 50 basis points is a recognition of the serious situation with respect to inflation in our country and the resolve to tackle inflation.
What is Cash Reserve Ratio?
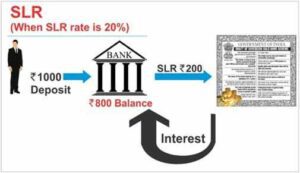
- It is a certain minimum amount of deposit that the commercial banks have to hold as reserves with the central bank.
- All Scheduled Commercial Banks are at present required to maintain with Reserve Bank of India a Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR) of 4.5% per cent of the Net Demand and Time Liabilities (NDTL) (excluding liabilities subject to zero CRR prescriptions) under Section 42(1) of the Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934.
What is Repo Rate?
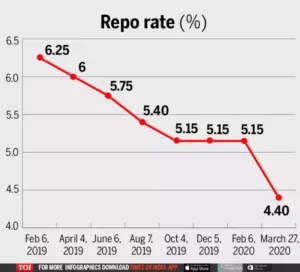
- Repo rate is the rate at which the central bank of a country (Reserve Bank of India) lends money to commercial banks.
- The RBI’s Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) has increased the policy Repo Rate by 40 basis points to 4.40%, with immediate effect.
What is GDP Deflator?
- The GDP deflator, also called implicit price deflator, is a measure of inflation. It is the ratio of the value of goods and services an economy produces in a particular year at current prices to that of prices that prevailed during the base year.
Challenges to Production?
- Following the implementation of COVID-19, officials all around the world were concerned about reviving demand. This was hoped to be accomplished by increasing government spending.
- The usual Keynesian prescription is as follows. Lockdowns were implemented to prevent the spread of COVID-19, which limited mobility.
- As a result, in countries where the lockdown was severe, increasing government spending did not instantly yield in greater production.
- When there were supply limits, as in developing countries, the Keynesian multiplier did not function, as V.K.R.V. Rao pointed out in the 1950s.
- Something similar happened in this situation, when the supply limitation was caused by the non-mobility of manufacturing elements.
What is happening around the World:
- Inflation became a problem when the economy gathered up steam in 2021-22 this is a worldwide phenomenon.
- Which is also true in the case of United States, The Federal Reserve’s balance sheet has exploded.
- The Fed’s total assets (minus certain things) were $4.17 trillion on January 1, 2020, and $8.96 trillion on April 1, 2022. The Fed’s quantitative easing programme, which effectively means liquidity support, has resulted in a tremendous asset boom.
- The Federal Bank Chairman has made strong pronouncements about the need to reduce asset size. The Federal ankB intends to reduce its balance sheet by $95 billion per month.
Source: THE HINDU.
For more update, click here to join our telegram channel




