Southwest monsoon begins early withdrawal in Rajasthan
#GS-01 Geography
For Prelims
About Monsoon:
- The term “monsoon” refers to the climate associated with the seasonal reversal of wind direction.
- The monsoons are a double system of seasonal winds that travel from the sea to the land in the summer and from the land to the sea in the winter.
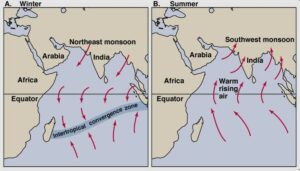
Monsoons in India occupy 2 divisions, namely.
The southwest monsoon season –
- Rainfall received from the southwest monsoons is seasonal in character, which occurs between June and September.
The retreating monsoon season –
- The months of October and November are known for retreating monsoons.
About ITCZ:
- The Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ) is a low-pressure belt that determines precipitation in the tropics by its northward and southward movements along the equator.
- This convergence zone lies parallel to the equator but moves north or south with the seasonal movement of the sun.
For Mains:
Factors Influencing Monsoon:
The differential heating and cooling of land and water:
- This creates a low pressure on the landmass of India while the seas around experience comparatively high pressure.
The shift of the position of Inter Tropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ):
- If the ITCZ in summer, moves over the Ganga plain i.e., the equatorial trough which is normally positioned about 5°N of the equator, it creates what is known as the monsoon-trough during the monsoon season.
The presence of the high-pressure area:
- High pressure area formed east of Madagascar, approximately at 20°S over the Indian Ocean. The intensity and position of this high-pressure area affect the Indian Monsoon.
The Tibetan plateau:
- If the Tibetan plateau gets intensely heated during summer, it will result in strong vertical air currents and the formation of low pressure over the plateau at about 9 km above sea level.
The movement of the westerly jet stream:
- Westerly jet stream moving to the north of the Himalayas and the presence of the tropical easterly jet stream over the Indian peninsula during summer.
Southern Oscillation (SO):
- Also known as El Nino, The presence of the El Nino leads to an increase in sea-surface temperatures and weakening of the trade winds in the region.




