Current Account Deficit
#GS-03 Economy
For Prelims:
About Current Account Deficit:
- The current account deficit is a measurement of a country’s trade where the value of the goods and services it imports exceeds the value of the products it exports.
- A current account deficit occurs when the total value of goods and services a country imports exceeds the total value of goods and services it exports.
- A current account deficit indicates that a country is importing more than it is exporting.
- The current account includes net income, such as interest and dividends, and transfers, such as foreign aid.
- The balance of exports and imports of goods is referred to as the trade balance. Trade Balance is a part of ‘Current Account Balance’.
- The current account represents a country’s foreign transactions and, like the capital account, is a component of a country’s balance of payments (BOP).
The formula to calculate CAD is:
Current Account = Trade gap + Net current transfers + Net income abroad
(Trade gap = Exports – Imports)
For Mains
Why in News?
- State Bank of India has pencilled in a lower current account deficit for India at 3%.
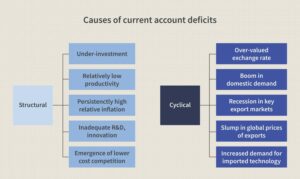
What caused the fall in CAD?
- Every ₹1 fall against the dollar leads to an increase in software exports by $250 million.
- This, along with an expected $5 billion-forex reserve accrual by way of swap transactions and higher remittances, will cap CAD at 3% of GDP.
- Strong remittances and software exports had pushed down CAD by 60 basis points (bps) in the June quarter.
- Software exports have been rising with the share of offsite mode of exports by domestic IT services firms soaring to 88.8% in FY22 from 82.8% five years earlier.